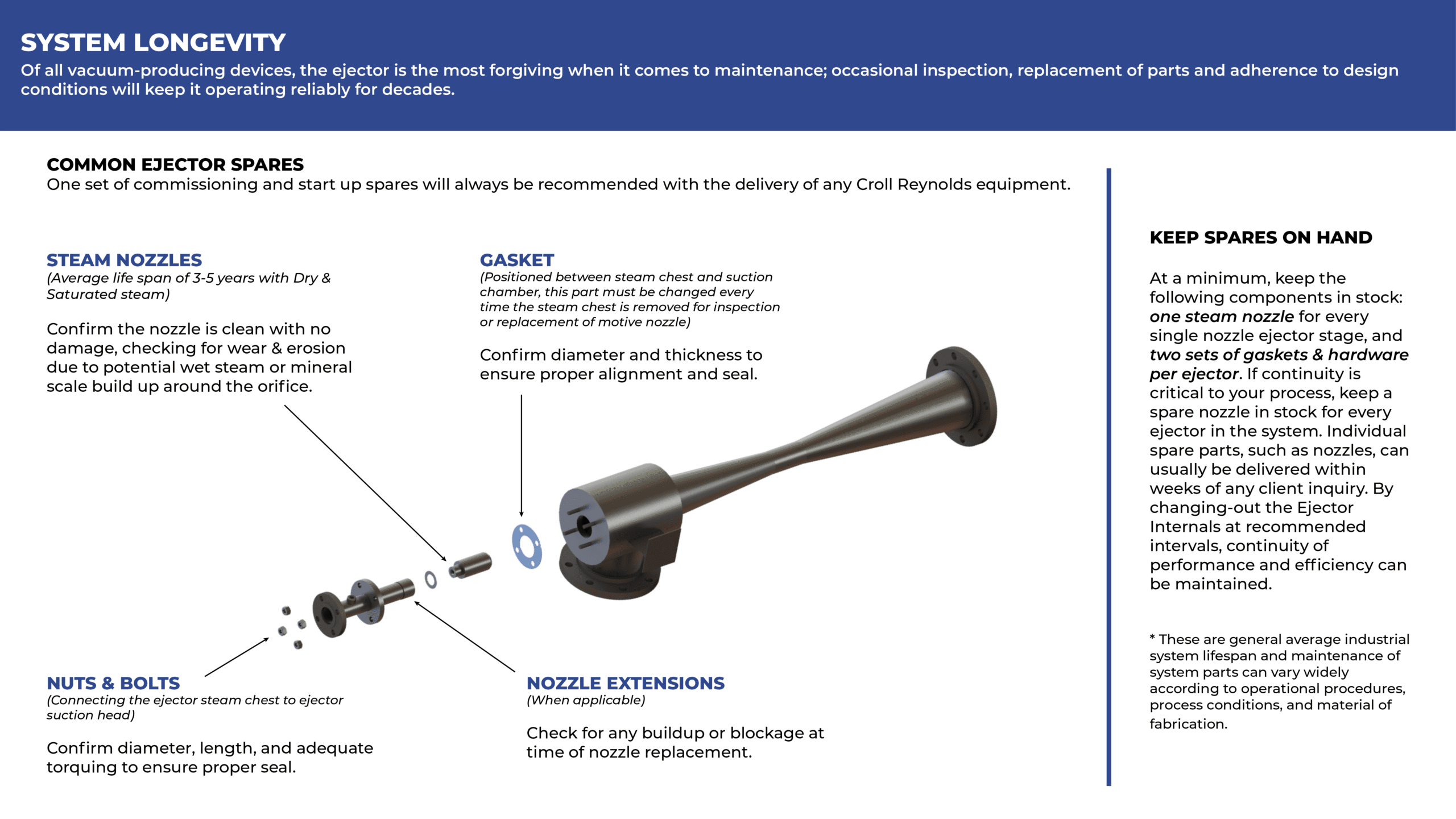
A jet condenser is a type of heat exchanger that uses Gas-Jet Cooling. In this process, a high-velocity stream of compressed air or inert gas is used to cool hot fluids. Jet condensers are commonly used in power plants and chemical plants. There are two types of jet condensers: direct contact and non-direct contact. each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. Let’s take a closer look at each type.
A jet condenser is a type of heat exchanger
The jet condenser is an amazing piece of technology that can help create some of the most efficient heating systems in the world. By allowing thermal energy to travel between two fluids, this type of heat exchanger allows for quick and efficient heat transfer with minimal wear and tear on the components of the system. Not only does this save time, but also money in terms of reduced energy costs. Additionally, it’s easy to install and maintain, making it one of the best methods of creating a reliable heating system. Make sure to consider this incredible technology if you’re in need of a great heating solution!
It’s used to transfer heat from one fluid to another
Heat exchangers provide an amazing service, they make it possible to transfer thermal energy between two applications, allowing the exchange of temperature-controlled fluids! They are a vital mechanical component when there is a need to transfer heat from one fluid to another while ensuring that they do not mix. For this reason, heat exchangers are incredibly useful and can be found in many different types of industrial settings in order to generate efficiency with minimal effort. All things considered, this invaluable technology has become increasingly important for modern-day applications and it’s worth taking a look at how heat exchangers operate.
There are three types of jet condensers – water-cooled, air-cooled, and oil-cooled.
Jet condensers are some of the most essential pieces of machinery when it comes to cooling systems. They come in three different types: water-cooled, air-cooled, and oil-cooled. Each type works differently and has its own advantages and drawbacks in terms of efficiency, cost, accessibility and size. Before buying a jet condenser for your industrial project, consider what your needs are to determine which one is right for you. With the right kind of jet condenser, you can make sure that your machines stay running cool and efficiently!
Water Cooled:
This type of jet condenser uses water as a cooling media to transfer the heat from one fluid to another. The main advantage of this system is its high thermal efficiency, meaning that it can transfer more heat with less energy input than other types of systems. This makes water-cooled jet condensers ideal for applications in power plants and other large industrial settings.
Air Cooled:
Air-cooled jet condensers use air as the cooling media, instead of water. This type is typically used in applications where a large amount of heat needs to be transferred quickly and efficiently, such as in some chemical processes. The main advantage of an air-cooled system is that it requires less energy input than a water-cooled system, making it an ideal choice for applications such as these.
Air-cooled jet condensers are less expensive than their water-cooled counterparts, but they’re not as durable. This is because air-cooled condensers rely on ambient air to cool the jet engine, while water-cooled condensers have a dedicated cooling system. Because of this, air-cooled condensers are more susceptible to damage from debris and other environmental factors.
Oil Cooled:
Oil-cooled jet condensers are the most efficient type of heat exchanger and are used in industrial settings when maximum heat transfer efficiency is required. In this type, oil is used as a cooling medium instead of water or air. This allows the system to transfer more heat with less energy input, making it ideal for situations where a very high level of efficiency is needed. Additionally, these systems are often used in power plants and other large-scale applications due to their ability to quickly transfer large amounts of heat.
Water-cooled jet condensers are the go-to choice for jet vacuum systems due to their impressive efficiency and long lifespan. Not only do they consume less power so electricity costs are minimal, but they also last up to 15 years with proper maintenance. This is great news for jet vacuum system owners since it means fewer time-consuming repairs and replacements over the years. In addition, these condensers use a closed loop of water or oil and don’t require much space or frequent attention, making them one of the most hassle-free solutions on the market today.
To sum it up, jet condensers are a great way to transfer heat between two fluids. Each type – water-cooled, air-cooled, and oil-cooled – has its own advantages and disadvantages to consider when choosing which one’s right for you. Water-cooled ones tend to be the most popular choice because of their efficiency, reliability, and long lifespan. Air-cooled varieties may be more economical but lack in durability compared to the water-cooled version. Remember to look over all your options before deciding – the right heat exchanger is out there waiting for you!
Get in touch with us
Related Posts
Understand the Working Principle of a Steam Ejector or Injector System

How Steam Ejectors Work: The Ultimate Guide
About Us
Croll Reynolds Company, Inc. is a US-based engineering firm specializing in the design, and manufacture of process vacuum systems and related equipment.